|
If the country or state you’re in observes summer time, then you’re either about to enter (if in the northern half of the marble) or leave it (if southern). To keep us on our toes, this movement back or forth often happens around the world on different dates. To keep us on our toes, some countries have less-than-hour gaps between time zones, and in the past, others have decided to change time zone permanently.
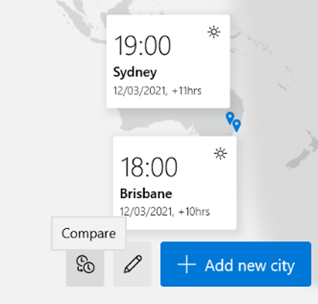
– eg if it’s 2:30am in Iran, then lining Tehran up with the red hand would put both London and Paris at midnight, since they’re both at GMT+1. eh? In October 1968, the UK decided to move to British Standard Time – GMT+1 – all year round. This particular wristwatch was produced between 1968 and the end of 1971, when the practice was reversed – so for a while, it was correct that London would be in the same time zone as Paris and Rome. Except the watch wouldn’t know when Paris and Rome went into summer time, thus putting them an hour further ahead… oh well, never mind. In a global working environment, especially one where everything is done online rather than having people in the same location, the friction of time zones changing has never been more obvious. Usually, you’ll only move through time zones relative to everyone else when you travel – flying across large distances, or maybe just driving across a bridge or dam. But now, a digitally-oriented meeting can shift its time for some of its attendees, relative to the others – depending on where the originator is based.
Those parts of the US which observe DST, are due to move an hour forward this coming Sunday (ie March 14th). In common with doing things differently to everywhere else, that brings the US (and Canada) one hour nearer most of Europe for the next two weeks, until the end of March. Much of the southern hemisphere comes out of DST the week after that, so by then Sydney will be two hours nearer London than currently. The impact of this can be seen in peoples’ calendars, when regular meetings somewhat inexplicably start to clash with each other – if a UK organiser set a recurring meeting for 4pm GMT, that would normally compel Seattleites to be there at 8am, but since they’ll be only 7 hours behind for a couple of weeks, that shifts to 9am in their calendar, potentially clashing with some existing 9am Pacific Daylight Time meeting. Conversely, a 9am PST / 5pm GMT meeting as created by the person in the US a few weeks ago, would now start at 4pm in the afternoon in London. Great news if that meeting is a Friday afternoon, as it brings beer o’clock one hour forward. Although Outlook does a pretty decent job of juggling the differences between time zones, there is no obvious way to show what time zone a meeting had been created in (eg show me all meetings that are going to be affected by this shift for the next 2 weeks). A simple trick if you want to check on a specific meeting, is to start a Reply to a meeting you’ve been invited to, whereupon you’ll see the time zone of its creator…
While It won’t help you identify the meetings that are causing the clashes, it might help restrain you from firing angry missives at the organiser of the meeting, if you know what’s causing it. |
Tag: Alarm
551 – Ticking away the moments
|
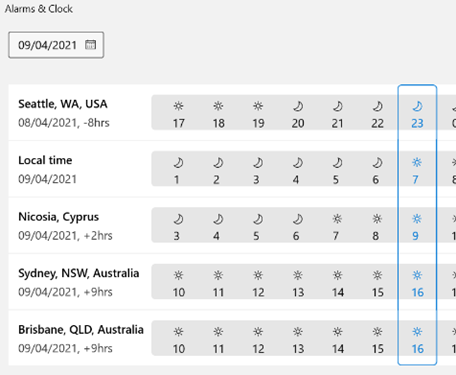
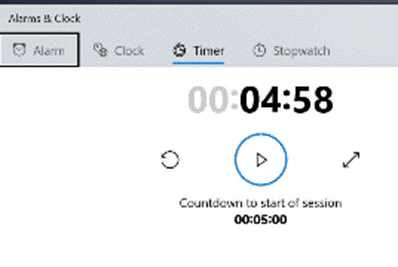
There’s a great little app built-in to Windows 10 called Alarms & Clock, which lets you set alarms on your PC, show a world map with multiple locations / time zones displayed, and also provides a neat countdown or count-up timer.
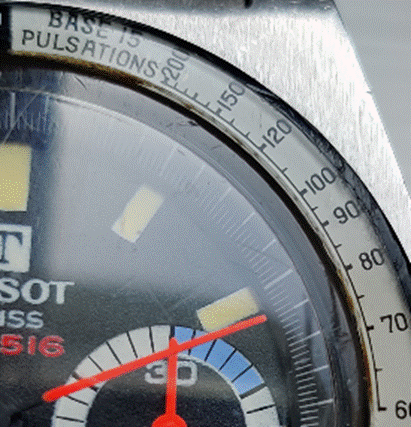
You can create multiple separately-controlled timers with different durations & names; so you could have an overall meeting countdown timer, and then a separate one for each participant, if you were acting as the time cop to keep everyone else in line. The Stopwatch is simply a fast-running counter of elapsed time, and by using the Those of us who still wear physical, mechanical wristwatches may be passingly familiar with a few features that have existed for decades to achieve the same kind of function, albeit more for individual rather than shared use. So called “diver” watches were popularised in the 1960s and 70s, as tough, waterproof and utilitarian. The most striking feature of any dive watch is generally the rotating numbered bezel which goes around the outside. The simple idea was that when you entered the water (knowing you might have 20 minutes of air), you would turn the bezel so the arrow / zero marker was set to where the minute hand was at that point – meaning a later glance at the watch will tell you how many minutes have passed since. Lots of other non-dive watches also have rotating bezels or indicators, and can be useful for things other than scuba – when the activity above started at 5 minutes to 10, the bezel was set, and it’s easy to see in a trice that was 11 or 12 minutes ago. Not sub-second accurate, but it’s a simple way to mark the passing of time. Many chronograph watches – which combine the function of a stopwatch and a regular timepiece – have a Tachymetre scale around the outside, yet most people these days will have no clue what it’s for. The basic function of the watch is that pusher buttons on the side will start and stop the movement of the chronograph hand which ticks round to indicate elapsed time. The deal with the TACHY scale is that if you know a distance – the length of a straight on a motor-racing track, for example – and you time something going over that distance, then you can quickly calculate its speed across the ground. In practice this is easier said than done, since the TACHY scale reads how many of the <distance> would be covered in an hour at this speed. If the measured distance was exactly 1km or 1mile then it’s an easy calculation – if it took 12 seconds to cover 1km, that would equate to 5km per minute or 300km/h. If the measured distance was a fraction – let’s say the length of the 12-second straight was 150m – then the calculation would be 300 x 150m per hour, or 45km/h. By the time you’ve done that in your head, the subject will be half a lap further on…
If you were cruising at 120km/h, and started the timer, then stopped it when it reached 120 on the scale… (after 30 seconds) – then you know you will have travelled 1km in that time. Yes, there probably are hundreds of times a month when you need to know exactly this. Pulsations
Watches with Pulsations bezels are sometimes nicknamed “Doctors’ watches” as the utility is to help count a patient’s pulse – the method being you start the chronograph, count 15 pulses and the corresponding number on the bezel would tell you what the pulse/minute rate is. Smart watches, eh, who needs them when you have space-age timing technology like this? |