 Snap is a feature in Windows, used to arrange applications on screen, building on a shortcut that has been around since Windows 7: press the Windows Key and one of the arrow keys simultaneously, and the current window will be maximised, minimised or snapped to one side of the screen. Windows 8’s touch fixation brought other means to control window layouts, while Windows 10 evolved things further with “Snap Assist”.
Snap is a feature in Windows, used to arrange applications on screen, building on a shortcut that has been around since Windows 7: press the Windows Key and one of the arrow keys simultaneously, and the current window will be maximised, minimised or snapped to one side of the screen. Windows 8’s touch fixation brought other means to control window layouts, while Windows 10 evolved things further with “Snap Assist”.
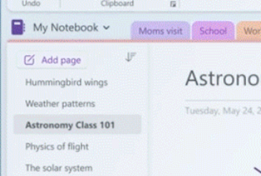
One of the improvements that came initially to Windows 11 and has been improved in the latest 22H2 update – imaginatively called the Windows 11 2022 Update – is the Snap Layouts feature, allowing finer control on the way you want windows to be arranged.
 Especially useful on high-res displays, this can be invoked by hovering the mouse over the maximise icon in the top right of any window, and choosing from a set of offered layouts.
Especially useful on high-res displays, this can be invoked by hovering the mouse over the maximise icon in the top right of any window, and choosing from a set of offered layouts.
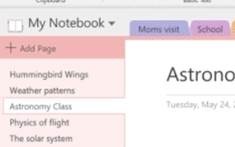
 You’ll then be able to select other open applications that can be slotted into the remaining screen space.
You’ll then be able to select other open applications that can be slotted into the remaining screen space.
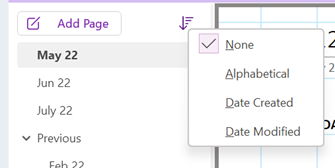
 This Snap Layout can also be invoked on the active window by pressing WindowsKey+Z, followed by a number key to represent the layout you want; press the corresponding number and then another
This Snap Layout can also be invoked on the active window by pressing WindowsKey+Z, followed by a number key to represent the layout you want; press the corresponding number and then another  number within the destination group, to quickly move the window – or Edge browser tab – to that location. This now creates a Snap group which shows up in the ALT+TAB gallery as if it was a single application, so making it easier to manage side-by-side windows that are related.
number within the destination group, to quickly move the window – or Edge browser tab – to that location. This now creates a Snap group which shows up in the ALT+TAB gallery as if it was a single application, so making it easier to manage side-by-side windows that are related.
![]() Finally, in the Windows 11 22H2 update, if you drag your window to the top of the screen, a small black bar will hove into view…
Finally, in the Windows 11 22H2 update, if you drag your window to the top of the screen, a small black bar will hove into view…
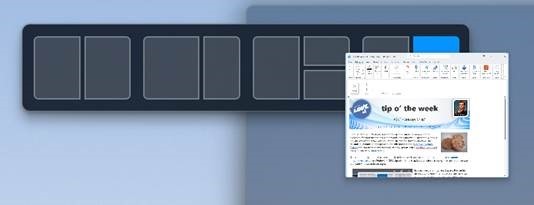 Continue dragging your window onto that as a target and a larger control will appear, allowing you to drop your window into the appropriate place. This also kicks off the Snap Assist feature which lets you easily select the other windows you’d like to be in the same layout.
Continue dragging your window onto that as a target and a larger control will appear, allowing you to drop your window into the appropriate place. This also kicks off the Snap Assist feature which lets you easily select the other windows you’d like to be in the same layout.
*Deceased muso George Michael famously pranged into a Snappy Snaps store, leading to some inspired graffiti.


![clip_image002[6] clip_image002[6]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0026_thumb.jpg)
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0044_thumb-1.gif)
![clip_image006[4] clip_image006[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0064_thumb-1.gif)
![clip_image008[4] clip_image008[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0084_thumb-1.gif)
![clip_image010[4] clip_image010[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0104_thumb-1.gif)
![clip_image012[4] clip_image012[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0124_thumb-1.gif)
![clip_image014[4] clip_image014[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0144_thumb.gif)




![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/clip_image0016_thumb.png)
![clip_image003[4] clip_image003[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/clip_image0034_thumb.png)
![clip_image005[4] clip_image005[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/clip_image0054_thumb.png)
![clip_image007[4] clip_image007[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/clip_image0074_thumb.png)
![clip_image009[4] clip_image009[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/clip_image0094_thumb.png)
![clip_image011[4] clip_image011[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/clip_image0114_thumb.png)
![clip_image013[4] clip_image013[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/clip_image0134_thumb.png)
![clip_image015[4] clip_image015[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/clip_image0154_thumb.png)
![clip_image002[4] Quick Assist logo](/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/clip_image0024_thumb.gif)
![clip_image004[4] Quick Assist update](/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/clip_image0044_thumb.gif)
![clip_image006[4] Sharing security code](/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/clip_image0064_thumb.gif)
![clip_image002[6] clip_image002[6]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/clip_image0026_thumb.gif)